(Visited 4,020 times, 1 visits today)
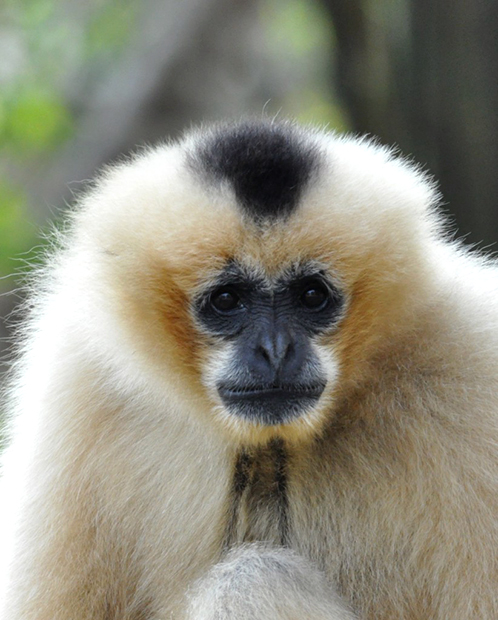
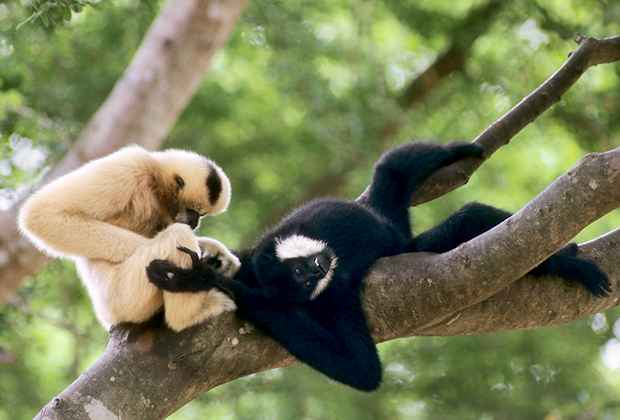
The male is black with a pronounced crest of fur on the crown and white cheek fur that extends continuously from the ears and under the chin. The adult females are beige to yellow with black faces and a patch of brown to black fur on the top of their head.
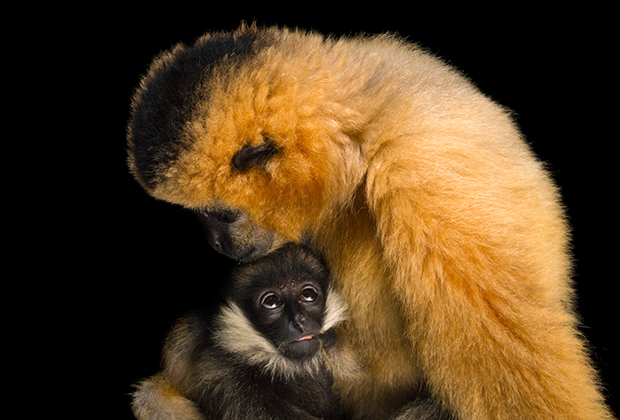
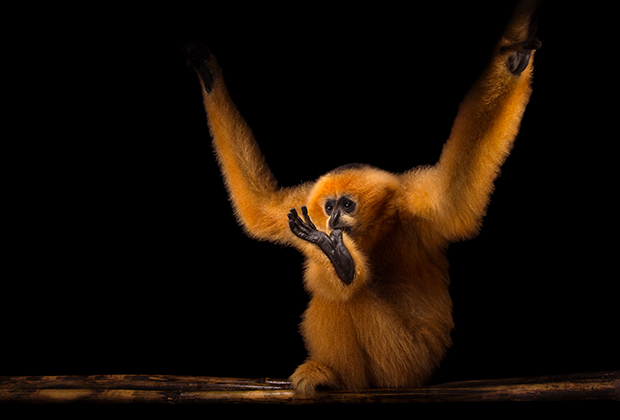
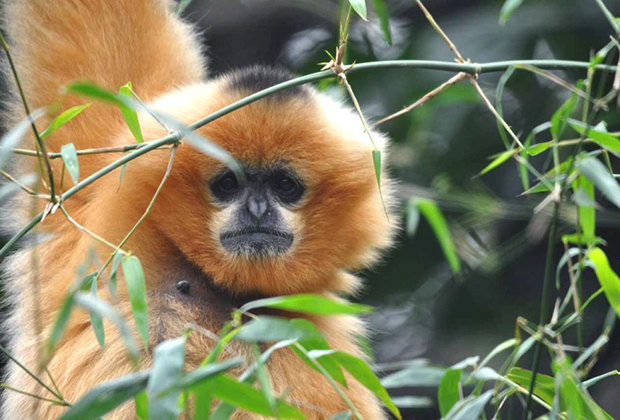
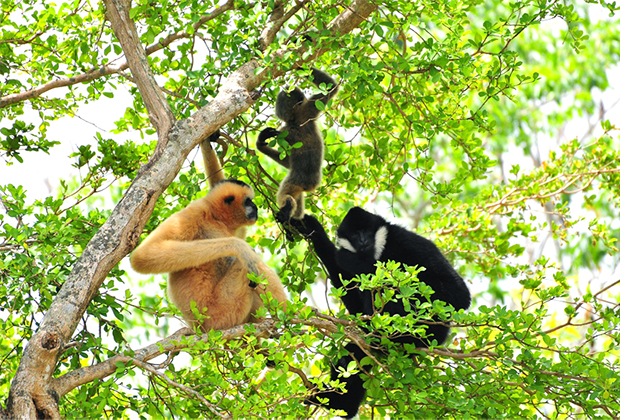




Found in Northwest Vietnam and Northern Laos, the species did occur until recently in Southern China but is most possibly already locally extinct there.
The Northern White-Cheeked Gibbon prefers lowland and lower montane evergreen forests, but they are currently restricted to higher altitudes due to encroachment pressure. Their diet is seasonal, comprising of various quantities of fruit, leaves, shoots, flowers, and insects. Like other gibbon species, they are territorial, living in monogamous pairs with immature offspring.
The main threat to this species is deforestation through agricultural encroachment into mountainous areas and the extraction of firewood and timber from the remaining forests, especially in China and Vietnam. Hunting for food, traditional “medicines” and the illegal pet trade is also a major threat across their range.
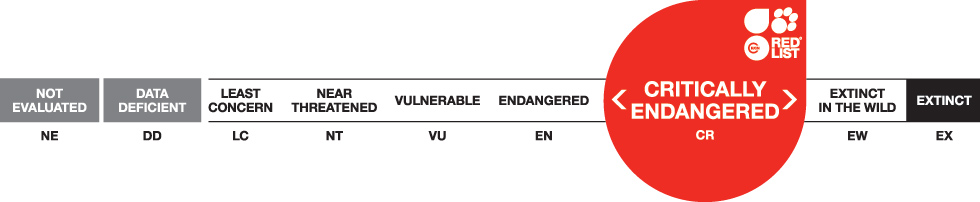
The species is protected across its range. In Vietnam, the Northern White-Cheeked Gibbon is listed in the 2007 Vietnam Red Data Book as ‘Endangered’ and is protected by law under Decree 32/2006 ND-CP: 1B.
This species is threatened with extinction and international trade is permitted only in exceptional circumstances.



Established in 1993, EPRC is a not for profit project dedicated to the rescue, rehabilitation, breeding, research and conservation of Vietnam’s endangered and critically endangered primate species.
© Endangered Primate Rescue Center 2020
Website by MINIMUMMEANS